
Ultimate Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Custom Web Application for Beginner’s in 2025
Imagine you own a business that has specific needs—maybe you want to connect better with customers, streamline your daily operations, or handle sales more efficiently. Now, think of a tool that does all that exactly the way you want. That’s what a custom web application does for you. Instead of fitting into a standard, ready-made solution, a custom web application is built specifically for your unique requirements. Here, we’ll walk through what a custom web application is, why it’s worth building one, and a step-by-step guide to help you understand how it’s developed.
What is Web Application Development?
In simple terms, a web application is a software you can use through your internet browser without installing it on your computer. Web applications are convenient because they’re accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. Think of popular web applications like Gmail for managing emails or Google Docs for creating documents. These are accessed through a browser and used over the internet.
Custom Web Application Development goes a step further by creating applications specifically tailored to your business needs. Unlike standard software that might come with extra features you don’t need or lack key features you do need, custom applications are designed just for you.
Why should you go for a custom web application development?
Custom web applications offer several benefits that off-the-shelf software might not. Here’s why they’re worth the investment:
1. Tailored to Your Needs: A custom web application is built specifically for your business, ensuring it fits your unique needs and goals.
2. Scalable as You Grow: A custom app can grow with your business, so you can add new features or handle more users easily as your business expands.
3. Better User Experience: Since it’s made for your audience, a custom app offers a smoother, user-friendly experience that keeps your customers engaged.
4. Enhanced Security: Custom web apps are designed with your business’s security needs in mind, making it harder for outsiders to access sensitive information.
5. Easy Integration: Custom apps can easily connect with your existing systems, whether it’s your accounting software, CRM, or other business tools.
6. Cost-Effective in the Long Run: Though it may seem expensive initially, a custom app saves costs over time with fewer upgrades and better efficiency.
7. Support and Maintenance: You get dedicated support, so if something goes wrong, it can be fixed quickly without waiting for general updates.
Steps to Building a Custom Web Application
Here’s a straightforward breakdown of how to build a custom web application. Each step is essential, and together they create a solution designed just for you.
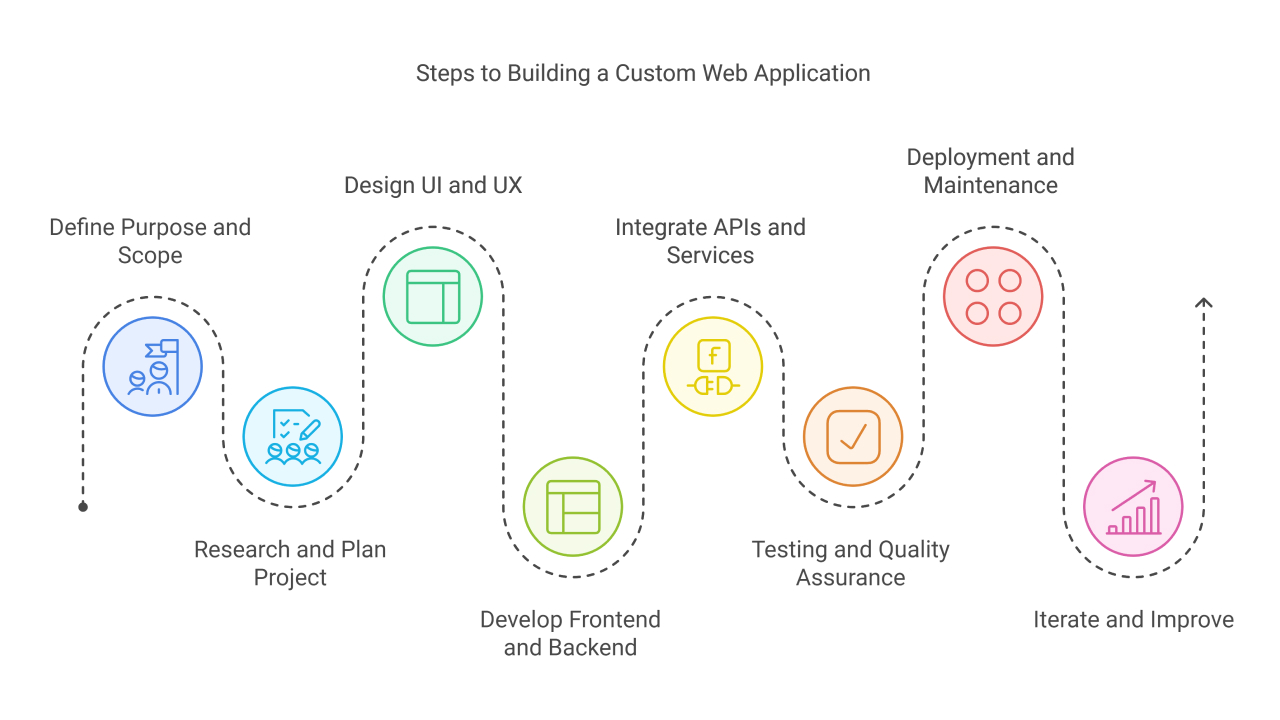
1. Define Your Purpose and Scope
Every successful web application begins with a clear understanding of its purpose. Ask yourself:
- What problem does the application solve?
- Who are the target users?
- What core features should the application include?
Example: Let’s say you run a small hotel. Your goal is to create an application where customers can book rooms, view amenities, and even check-in online. Here, your target users are both new and returning guests, and your features should include booking, room selection, and check-in.
Set a Budget and Timeline: It’s important to know your budget and expected time for completion. A well-planned budget helps avoid surprises later on.
2. Research and Plan Your Project
Competitive Analysis: Look at similar apps to understand what’s already out there. This will give you ideas on what works well and what could be improved.
Choosing the Right Tech Stack: Your tech stack – the combination of programming languages, frameworks, and tools – defines how your application will be built, scale, and perform. Here’s a basic overview of a typical tech stack for a web application:
- Frontend (User Interface): HTML, CSS, and JavaScript frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js.
- Backend (Server-Side Logic): Languages like Node.js, Python, PHP, or Ruby and frameworks like Express, Django, or Laravel.
- Database (Data Storage): Choose between relational databases (MySQL, PostgreSQL) and NoSQL databases (MongoDB, Firebase) based on your data structure needs.
Design a Blueprint: Before development begins, create basic sketches or wireframes. Wireframes help you visualize how users will interact with your application.
3. Design the User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX)
A good design isn’t just about looking pretty—it’s about making the application easy to use.
Example: Suppose you’re creating an application for restaurant reservations. The UI should show options like date, time, and table preferences clearly. Each option should be intuitive, so users can complete a reservation quickly without frustration.
Mock-ups and Prototypes: These are early designs that simulate the app’s look and feel. They’re used to gather feedback from stakeholders and improve the design before actual development begins.
4. Develop the Frontend and Backend
Frontend Development: This part of development focuses on what users see and interact with, including layout, color, fonts, and forms.
Backend Development: The backend handles the “behind-the-scenes” work. The backend is the core engine of your application. This is where user authentication, data processing, and business logic are implemented. Important backend tasks include:
- Database Setup: Define data schemas, tables, and relationships.
- API Development: Build APIs to allow the frontend to communicate with the backend. REST or GraphQL are popular API standards.
- Authentication & Security: Ensure user data is secure with authentication measures (e.g., JWT, OAuth) and data encryption.
For example, if your app is an online store, the backend manages the product listings, orders, payments, and user data. Backend development involves setting up the database, server, and any required APIs.
5. Integrate APIs and Third-Party Services
Many applications use APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) to bring in additional features. APIs can connect your application to services like payment processors, messaging platforms, or even social media logins.
Example: If you’re building an app that lets users book appointments, you might use an SMS API to send them reminders. Or, for a shopping app, you could use a payment API to securely process transactions.
6. Testing and Quality Assurance
Testing is essential to catch any issues and ensure everything works smoothly.
Functional Testing: Each feature should be tested to ensure it works as expected. For example, if users are supposed to receive a confirmation email after booking, make sure it happens every time.
Performance Testing: Assess speed and responsiveness.
Usability Testing: This ensures the application is easy to navigate. If users find it confusing or challenging to complete basic tasks, it’s time to rethink the design.
Security Testing: Security is a top concern, so testing for vulnerabilities, such as weak password options, is critical.
7. Deployment and Maintenance
Once testing is complete, deploy the application to a hosting environment. Platforms like AWS, Heroku, or Digital Ocean offer reliable hosting options. Don’t forget to set up continuous integration (CI) and continuous deployment (CD) pipelines for regular updates.
Choose Reliable Hosting: Hosting is where your application will live online. Options like AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure are commonly used for web apps.
Deployment: First, deploy in a staging environment, which is a test version of your app, then move to production (live version) when it’s ready.
Ongoing Monitoring: After deployment, monitoring tools like Google Analytics or New Relic help track how users interact with your app. This data can be used to fix bugs, improve user experience, and update features.
8. Iterate and Improve
Your custom web application will need regular updates as user needs evolve. Gather feedback from users and improve the application based on their input. For instance, if many users request a new feature, consider adding it in a future update.
How Revalsys Custom Web Applications Benefit Businesses
Revalsys specializes in creating custom web applications tailored to your specific business needs. Here’s how our solutions can help:
1. Tailored Solutions: Each application is designed to suit the unique workflows, goals, and challenges of your business, ensuring that you get maximum value.
2. Performance-Optimized: Our applications are built to handle large volumes of data and provide insights in real time, making them ideal for data-heavy industries.
3. Strong Integrations: Our applications are made to work smoothly with your existing tools and software, so your entire tech ecosystem functions as one unit.
4. High Security: Security is a top priority. We use the latest security protocols to protect your data and ensure the privacy of your users.
5. Scalable for Growth: Revalsys applications are designed with scalability in mind, allowing you to add more users and features as your business expands.
Conclusion
Creating a custom web application is a step-by-step process that, when done right, can bring immense value to your business. Unlike off-the-shelf software, custom applications are designed specifically to address your business’s needs, allowing for enhanced efficiency, improved customer experience, and seamless integration. If you’re considering building a custom application, Revalsys can help make this process easy, guiding you from concept to deployment. With the right plan and approach, your custom web application can become an invaluable tool that grows and adapts with your business.
